Silage Corn Nitrogen Uptake and Partitioning
Crops:
Almonds
Barley
Broccoli
Cauliflower
Citrus
Corn for Grain
Corn for Silage
Cotton
Grapevines
Lettuce
Pistachio
Rice
Strawberries
Tomatoes
Walnut
Wheat
Seasonal N Uptake
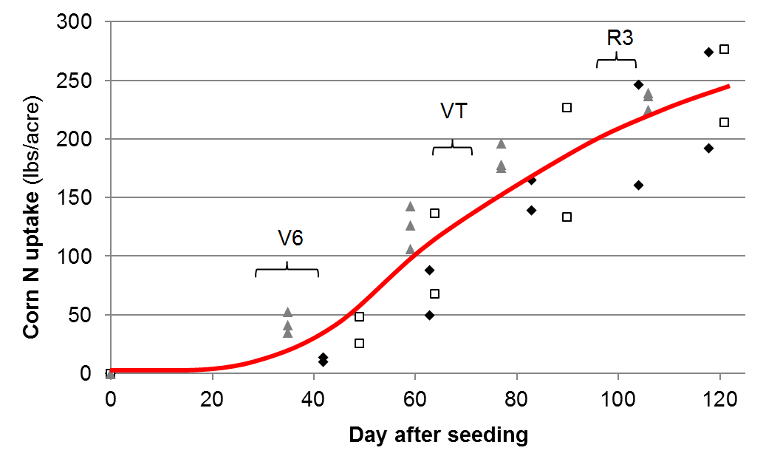
Nitrogen uptake curve of silage corn grown on three dairies in
the Modesto area. Uptake was determined by harvesting the
aboveground biomass at different times during corn
development.
Corn plants took up little N until they reached the 6-leaf stage (V6). Between the 6-leaf and the milk stage (R3), however, N uptake rates were high. When corn reached the tasseling stage (VT), it had taken up 60% or more of the total N. (Geisseler et al., 2012).
Nitrogen Partitioning
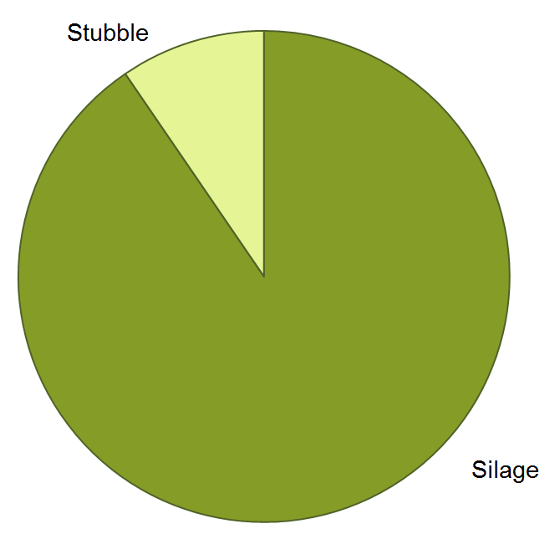
Almost the entire aboveground biomass is removed when silage
corn is harvested. We estimated that less than 10% of the
aboveground N is left in the field with the stubble.
Nitrogen Removed at Harvest
Yield and N removed from the field with silage corn based on
measurements taken in fields of dairies in the Modesto area.
In an extensive review, Ciampitti and Vyn (2012) found that
aboveground biomass of modern corn varieties contains on
average 0.93% N, which corresponds to 18.6 lbs/ton.
Links
References
Ciampitti, I.A., Vyn, T.J., 2012. Physiological perspectives of changes over time in maize yield dependency on nitrogen uptake and associated nitrogen efficiencies: A review. Field Crops Research 133, 48–67.
Geisseler, D., Lazicki, P.A., Pettygrove, G.S., Ludwig, B., Bachand, P.A.M., Horwath, W.R., 2012. Nitrogen dynamics in irrigated forage systems fertilized with liquid dairy manure. Agronomy Journal 104, 897-907.
